04th Nov , 2020
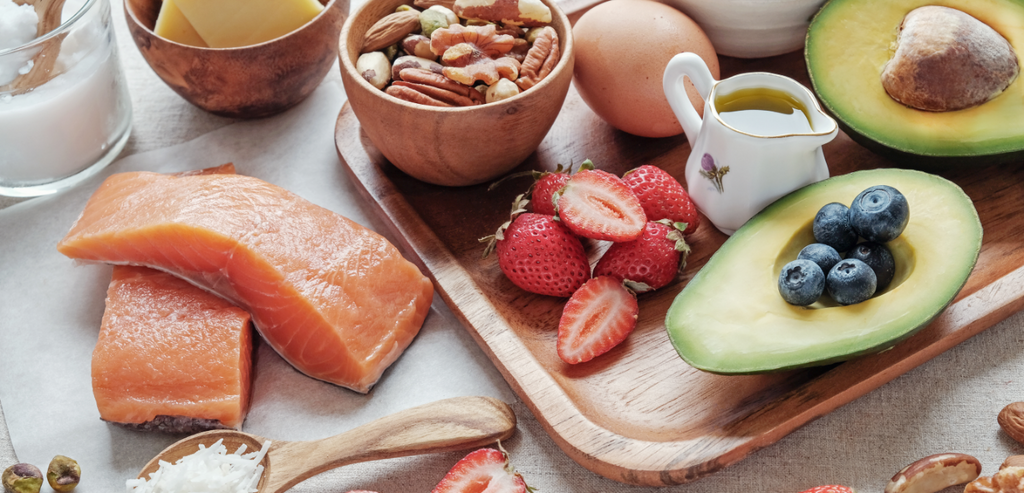

If searches are anything to go by, you’re probably already well versed in the ketogenic ‘keto’ diet and how it works. According to Google New Zealand, The high-fat, low-carb diet was one of the top searched diets of 2019 – and for good reason, the results are proven effective.
For keto beginners, the name comes from the goal of the diet: to get your body to a state of ketosis, where you burn fat for energy rather than carbs, which leads to weight loss.
What is the ketogenic diet?
A ketogenic diet is very low in carbohydrates and moderate in protein, meaning a high percentage of total energy (kilojoule) intake comes from fat rather than carbs. It doesn’t mean loading up on red meat and butter – it’s all about fuelling the body with healthful fats.
The benefits of keto are far reaching ranging from the more renowned like weight loss and boosted metabolism, to more surprising benefits like improved brain function and reduced risk of disease. Still need convincing? Gwyneth Paltrow, Kim Kardashian, Halle Berry, Lebron James and Megan Fox are just a few of the celebrities who have pledged themselves to the keto lifestyle.
How keto works
As fat is the main source of energy being consumed, the body must utilise this as its primary source of 'fuel'. When dietary fat is metabolised for energy, by-products called ketone bodies (molecules that are made by the liver from fatty acids) are produced, which are used up by the body's tissues, muscles and the brain. This process is known as ketosis.
The body can enter ketosis during times of energy restriction (such as during fasting or starvation), prolonged intense exercise or when carbohydrate intake is reduced to around 50g per day, or less – the equivalent of around two slices of bread and a banana.
What you can eat on the keto diet?
There’s a common misconception that the keto diet is extremely restrictive – just high intake of meat, eggs and cheese - and not suitable for vegetarians. However, that’s not the case, in fact there really is no end to the meals you can create. From Mexican low carb keto tacos to Indian chicken coconut curry, to delicious guilt-free desserts like keto waffles and chocolate mousse, all bursting with flavour to rival their carb-laden counterparts. Thankfully, with the rise in popularity, there’s now heaps of convenient ready-to-eat keto pantry staples and snacks on the market, like our cookies and bread!
So, where do you start?
If you’re a beginner and wondering how to start keto, consult our top tips below…
- Start simple
Don’t over complicate things in the beginning, there’s plenty of time to experiment with more complex gourmet recipes down the track. Adhere to a simple framework for meals like the below…
- Pick a protein: chicken, beef, eggs etc.
- Pick a low carb vegetable: broccoli, brussel sprouts, cucumber, capsicum etc.
- Add fat: cheese, butter, mayo, avocado etc.
- Make a meal plan
We find prepping as much in advance as possible makes sticking to keto super easy. The less last minute thinking required the better!
- Find substitutions for common pantry staples like coconut oil instead of olive oil
- Remove temptations from the house
It’s much easier to stick to your goals if you’re not constantly fighting temptation. Get rid of foods high in sugar and carbs, as well as starchy vegetables.
- Ease into it
As with any new way of eating, you may experience some initial side effects such as fatigue. Don’t put too much pressure on yourself to exercise every day – just take it one day at a time to start.
- Know what you can and can’t eat
Below is a snapshot of the foods that have the keto tick of approval:
- Meat
- Poultry
- Fish and seafood
- Low carbohydrate vegetables e.g. broccoli, cauliflower, zucchini, spinach
- Low carbohydrate fruits e.g. strawberries, blueberries, avocado
- Small amounts of moderate carbohydrate vegetables such as carrot (when the daily carbohydrate count allows)
- Nuts and seeds, like macadamia and pecan, in moderation
- Oils (olive oil, coconut oil, avocado oil)
- Low carbohydrate dairy products e.g. cream, cheese, some yoghurts
- Low/no calorie sweeteners such as stevia
Foods that are usually excluded are:
- Grains including wheat, barley, rice, oats and corn
- Legumes e.g. chickpeas, lentils, beans
- Pseudograins e.g. quinoa, buckwheat
- High carbohydrate vegetables e.g. sweet potato, potato
- High carbohydrate fruits e.g. bananas, mangos, dates, watermelon
- Soft drinks sweetened with sugar
- Processed foods with a high carbohydrate content e.g. baked goods and chips
Other Articles

09th Nov , 2020
Benefits of Keto
Thinking of starting keto? Then you’ve come to the right place! A ketogenic diet is a low-carb, high-fat and moderate-protein diet that alters the body’s metabolism to use fat as the preferred fuel, rather than sugars.